Explanation: Answer option C is correct.A Pareto chart is a special histogram in that it shows categories of failures from the largest failure to the smallest failure. The idea is that the project team or organizational development team will attack the largest problems first.
Pareto chart
A Pareto chart is a special type of bar chart where the values being plotted are arranged in descending order. The graph is accompanied by a line graph, which shows the cumulative totals of each category, left to right. The chart is named after Vilfredo Pareto, and its use in quality assurance was popularized by Joseph M. Juran and Kaoru Ishikawa.A Pareto chart is a histogram where items (such as number of defects) are ordered by frequency of occurrence, as shown in the below example:
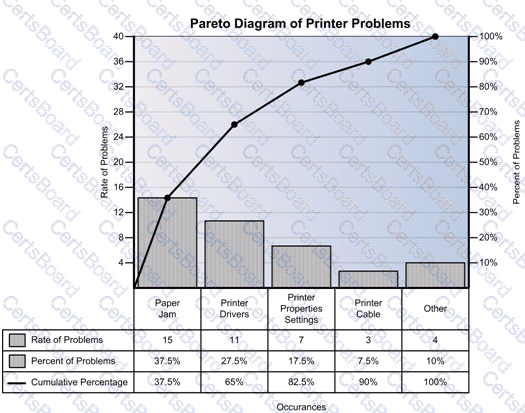
Example of a Pareto chart
It is a type of chart that consists both bars and a line graph, where individual values are represented in descending order by bars, and the cumulative total is shown by the line.
Answer option A is incorrect. A histogram is simply a bar chart and isn't ordered from largest to smallest.Answer option D is incorrect. A fishbone diagram is also known as an Ishikawa diagram or a cause and effect chart.
Ishikawa diagram
The Ishikawa diagram (or fishbone diagram or also cause-and-effect diagram) is a diagram that shows the causes of a certain event. A common use of the Ishikawa diagram is to identify potential factors causing an overall effect. It helps identify causal factors and root causes. 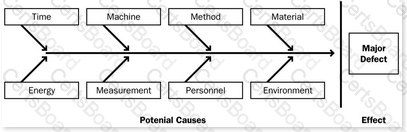 It is known as a fishbone diagram because of its shape, similar to the side view of a fish skeleton. It is considered as a basic tool of quality management.
It is known as a fishbone diagram because of its shape, similar to the side view of a fish skeleton. It is considered as a basic tool of quality management.
Answer option B is incorrect. A control chart shows trend analysis by tracking the results of measurements over time.
What are control charts?
Control charts are graphical representations of different processes. These charts contain the maximum and minimum values allowed. Control charts are used to determine whether or not a process is stable or has predictable performance. A process is considered out of control when a data point exceeds a control limit or if seven consecutive points are above or below the mean.


