Refer to the following figure of the ACL configured on a router. Which of the following statements is true?
nginx
CopyEdit
acl number 2000
rule 5 permit source 192.168.1.1 0
rule 10 deny source 192.168.1.1 0
Which of the following is correct regarding the configuration of the trunk port and access port on a switch?
Which of the following protocols can be used to prevent Layer 2 loops on a campus network?
To enable Router A to communicate with Loopback 0 on Router B on the network shown in the figure, which of the following commands needs to be run on Router A?

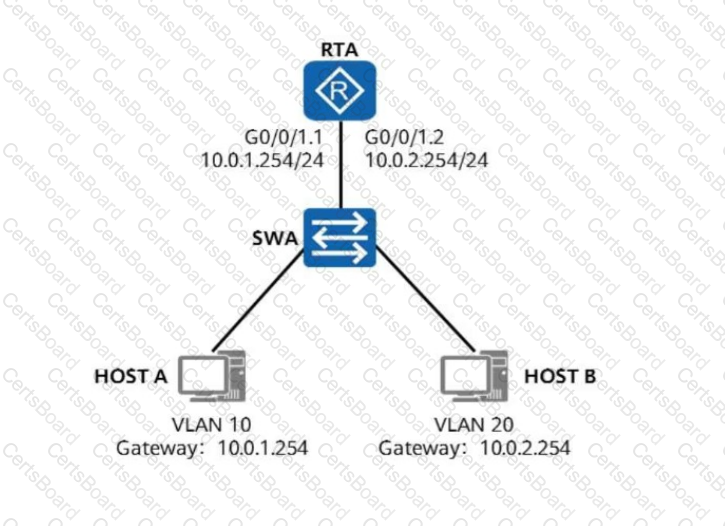
On the network shown in the figure, HOST A and HOST B are required to communicate with each other across VLANs through one-armed routing. To satisfy this requirement, which of the
following commands needs to be performed on G0/0/1.1 of RTA?
By referring to the topology and the configurations of G0/0/1 interfaces on LSW1 and LSW2 shown in the figure, it can be determined that data frames tagged with VLAN 10 can be normally forwarded between LSW1 and LSW2.
A Layer 2 switch works at the data link layer. As such, it can identify MAC addresses in data frames, forward data based on MAC addresses, and record mappings between MAC addresses and interface numbers in its MAC address table.
While inspecting packets in the network, a network administrator discovers a frame with the destination MAC address of 01-00-5E-A0-B1-C3. What can the administrator determine from this?
In standard STP mode, which of the following ports on non-root switches forward the BPDUs with TC bits set generated by the root switch?