Which of the following configurations are not mandatory when an administrator configures VRRP?
During routine maintenance, an enterprise administrator runs a command to check VRRP group information. Which of the following statements is false about the command output?
yaml
CopyEdit
Vlanif100 | Virtual Router 1 State: Master
Virtual IP: 10.1.1.100
Master IP: 10.1.1.2
PriorityRun: 120 PriorityConfig: 120
DR: None BDR: None MTU: 0
Preempt: YES Delay Time: 20s
Remain: --
Track: YES Priority Reduced: 20
Auth Type: MD5
BFD-session State: UP
On a network, each router has a local core routing table and protocol routing tables. A routing entry in the local core routing table has multiple key fields. Which of the following are included?
In inter-AC roaming scenarios, an AC can function as the mobility server of multiple mobility groups, but can be added only to one mobility group.
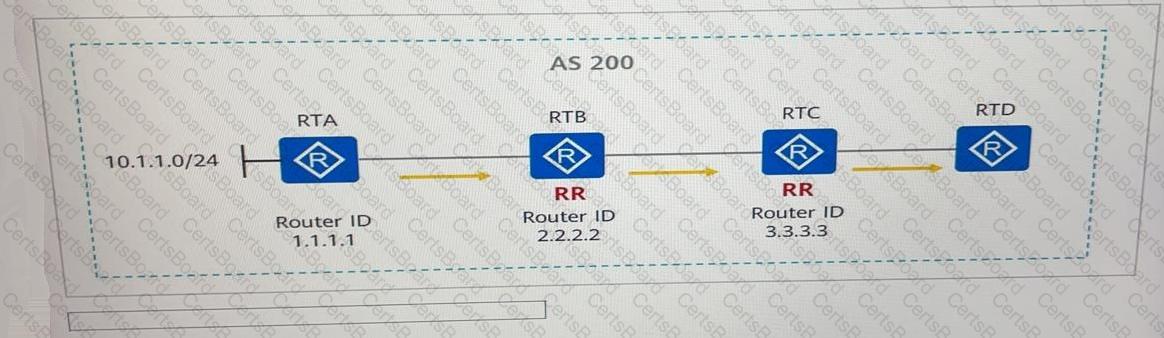
See the following figure. RTA, RTB, RTC, and RTD are in the same AS and establish IBGP peer relationships through direct links. RTB an RTC are route reflectors (RRs), RTA and RTC are the RR clients of RTB, and RTB and RTD are the RR clients of RTC. If RTA advertises the route 10.1.1.0/24 to the BGP process, the Originator ID of the BGP route received by RTD is------------------.
On an STP network, the root bridge, root port, and designated port are elected in sequence. The election rules of these ports are different. List the steps for electing the root port in sequence.
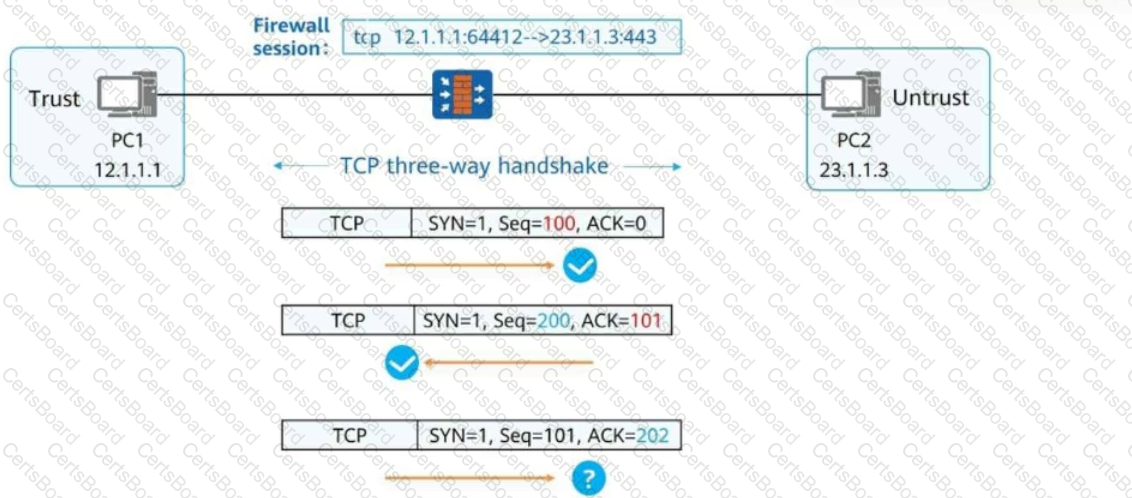
As shown in the figure, the stateful inspection firewall forwards the packet because the packet matches the session status of the firewall.