GET 70% Discount on All Products
Coupon code: "Board70"
XYZ is a large and successful airline which is looking to expand into a new geographical market. It currently offers short haul flights in Europe and wishes to expand into the Asian market. In order to do this, the CFO is considering medium/ long term financing options.Describe 4 options that could be used.
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Four Medium/Long-Term Financing Options for XYZ’s Expansion into Asia
Introduction
Expanding into anew geographical marketrequiressignificant capital investmentfornew aircraft, operational infrastructure, marketing, and regulatory approvals. As XYZ Airlines plans to enter theAsian market, the CFO must assessmedium and long-term financing optionsto fund this expansion while managing risk and financial stability.
The following arefour key financing optionsthat XYZ can consider:
1. Bank Loans (Term Loans)????
Definition
Abank term loanis a structured loan from a financial institution with afixed repayment period (typically 5–20 years), used for large-scale business investments.
✅Advantages✔Predictable repayment structure– Fixed or floating interest rates over an agreed period.✔Retains company ownership– Unlike equity financing, no shares are sold.✔Can be secured or unsecured– Flexible terms depending on company creditworthiness.
❌Disadvantages✖Requires collateral– Airlines often secure loans against aircraft or other assets.✖Fixed repayment obligations– Risky if revenue generation is slower than expected.✖Interest rate fluctuations– Increases costs if rates rise (for variable-rate loans).
????Example:
British Airways secured bank loansto fund new aircraft purchases.
????Best for:Large capital expenditures, such as purchasing aircraft for the new Asian routes.
2. Corporate Bonds????
Definition
Acorporate bondis adebt security issued to investors, where the company borrows capital and agrees topay interest (coupon) over timebefore repaying the principal at maturity (typically 5–30 years).
✅Advantages✔Large capital raise– Bonds can generate substantial long-term funding.✔Lower interest rates than bank loans– If the company has a strong credit rating.✔Flexibility in repayment– Interest payments (coupons) are pre-agreed, allowing financial planning.
❌Disadvantages✖High creditworthiness required– Investors demand a solid credit rating.✖Fixed interest costs– Even in poor revenue periods, interest payments must be met.✖Long approval and issuance process– Complex regulatory and underwriting procedures.
????Example:
Lufthansa issued corporate bonds to raise capital for fleet expansion.
????Best for:Funding fleet expansion or infrastructure development without immediate repayment pressure.
3. Lease Financing (Aircraft Leasing)✈️
Definition
Lease financing involvesleasing aircraft instead of purchasing them outright, reducing initial capital expenditure while maintaining operational flexibility.
✅Advantages✔Lower upfront costs– Avoids large capital outlays.✔More flexible than ownership– Can return or upgrade aircraft as market demand changes.✔Preserves cash flow– Payments are spread over time, aligning with revenue generation.
❌Disadvantages✖Higher long-term costs– Leasing is more expensive over the aircraft’s lifespan compared to ownership.✖Limited asset control– XYZ would not own the aircraft and must follow leasing conditions.✖Dependent on lessors’ terms– Strict maintenance and usage clauses.
????Example:
Ryanair and Emirates use operating leases to expand their fleets cost-effectively.
????Best for:Entering new markets with minimal financial risk, allowing XYZ to test the Asian market before making major capital investments.
4. Equity Financing (Share Issuance)????
Definition
Equity financing involves raising funds byissuing new company shares to investors, providing long-term capital without repayment obligations.
✅Advantages✔No repayment burden– Unlike debt, there are no interest payments or fixed obligations.✔Enhances financial stability– Reduces leverage and improves balance sheet strength.✔Can attract strategic investors– Airlines may raise capital frompartners or industry investors.
❌Disadvantages✖Dilutes ownership– Existing shareholders lose some control.✖Time-consuming approval process– Requires regulatory compliance and investor confidence.✖Market dependence– Success depends on stock market conditions.
????Example:
IAG (British Airways' parent company) raised capital via a share issuance to fund expansion.
????Best for:Companies looking for long-term funding without increasing debt, especially if stock market conditions are favorable.
5. Comparison of Financing Options
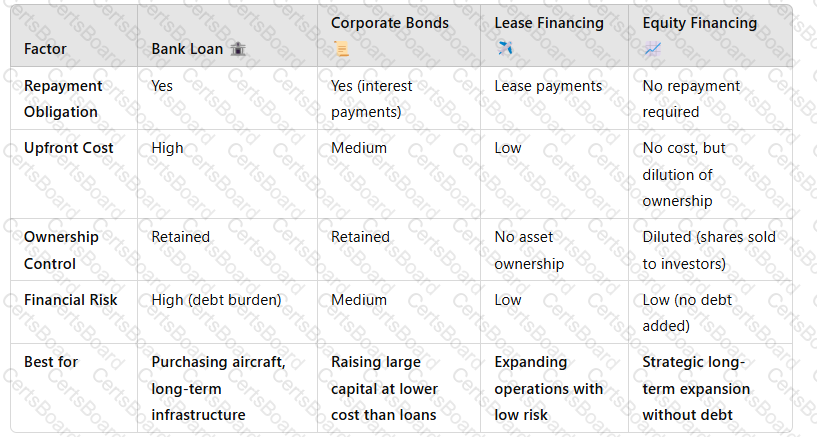
Key Takeaway:Each financing option suits different strategic needs, from ownership-based expansion to flexible leasing.
6. Recommendation: Best Financing Option for XYZ’s Expansion
✅Best Option: Lease Financing (Aircraft Leasing)✈️
Minimizes financial riskwhile expanding into Asia.
Avoids large upfront costs, preserving cash for operations.
Allows flexibilityif the new market underperforms.
Alternative Approach: Hybrid Strategy
Lease aircraft initially→ Test the Asian market.
Issue corporate bonds later→ Secure long-term funding for growth.
Consider equity financingif a strategic investor is interested.
????Final Takeaway:A combination ofleasing for operational flexibilityandcorporate bonds or equity for long-term financial strengthis the best approach for XYZ’s expansion into Asia.
Discuss how the following can impact upon supply chain operations and business strategy:
1) Discrimination, equality and diversity
2) Redundancy and dismissal
3) Working time and payment
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Impact of Employment Policies on Supply Chain Operations and Business Strategy
Introduction
Employment policies such asdiscrimination, equality and diversity, redundancy and dismissal, and working time and paymenthave a significant impact onsupply chain operations and business strategy. These factors influenceemployee productivity, legal compliance, reputation, and operational efficiency.
For businesses operating inglobal supply chains, ensuring compliance withemployment laws and ethical workforce practicesis crucial to maintainingsustainability, cost efficiency, and risk management.
1. Impact of Discrimination, Equality, and Diversity on Supply Chain Operations and Business Strategy
Discrimination laws anddiversity and inclusion (D&I) policiesensure fair treatment in the workplace.
✅Impact on Supply Chain Operations
Companies mustprevent workplace discriminationacross hiring, promotions, and supplier engagement.
Non-compliance withequality lawscan lead tolegal penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
Supply chain leaders mustpromote diverse supplier partnershipsand inclusive hiring practices.
????Example:Many multinational corporations, such asUnilever and IBM, havesupplier diversity programsthat prioritize working withminority-owned and women-owned businesses.
✅Impact on Business Strategy
Encouragesinnovation and diverse perspectivesin problem-solving.
Enhancesbrand reputation and customer loyaltythrough ethical business practices.
Helps businesses attracttop global talentby fostering an inclusive workplace.
????Strategic Action:Businesses should implementanti-discrimination traininganddiversity recruitment strategiesto create a fair and inclusive work environment.
2. Impact of Redundancy and Dismissal on Supply Chain Operations and Business Strategy
Redundancy and dismissal policies regulate how companiesterminate employment due to economic downturns, automation, or restructuring.
✅Impact on Supply Chain Operations
Workforcereductions can disrupt production schedules and supplier relationships.
Companies must ensurefair redundancy policiesto prevent legal claims or industrial action.
Automation may lead toworker displacement, requiringretraining programs.
????Example:Ford’s decision to restructure operations in the UKresulted in job losses, requiring compliance withUK redundancy lawsand union negotiations.
✅Impact on Business Strategy
Must balancecost-cutting measureswith employee morale and brand reputation.
Need to comply withnational and international labor lawsto avoid legal action.
Investing inemployee retraining and redeploymentcan reduce negative effects of redundancy.
????Strategic Action:Businesses should establishclear redundancy frameworks, provideseverance packages, and offeroutplacement supportfor affected employees.
3. Impact of Working Time and Payment on Supply Chain Operations and Business Strategy
Working time regulations and fair wage policiesimpact labor costs, productivity, and compliance.
✅Impact on Supply Chain Operations
Ensuring compliance withworking time laws (e.g., UK Working Time Regulations 1998)prevents overworking employees.
Failure to meetminimum wage and overtime regulationscan lead to legal disputes.
Supply chains must ensurefair pay for workers in offshore factoriesto meetethical sourcing standards.
????Example:TheUK National Minimum Wage Actensures fair wages, while theModern Slavery Act (2015)prevents exploitation in global supply chains.
✅Impact on Business Strategy
Fair wages enhanceemployee motivation and reduce turnover.
Complying withwage and hour lawsprevents reputational risks and fines.
Ethical pay practices attractconscious consumers and investors.
????Strategic Action:Businesses should conductregular wage auditsand ensureglobal supplier compliance with fair labor laws.
Conclusion
Employment policies related todiscrimination, redundancy, and working time/paysignificantly impactsupply chain operations and business strategy. Companies must ensure:
✅Diversity and equality policiesto foster innovation and enhance reputation.✅Ethical redundancy and dismissal processesto maintain legal compliance.✅Fair wages and working hoursto improve productivity and worker well-being.
By aligning HR policies with supply chain strategy, businesses canenhance efficiency, reduce risks, and build a sustainable competitive advantage.
XYZ is a toilet paper manufacturer based in the UK. It has 2 large factories employing over 500 staff and a complex supply chain sourcing paper from different forests around the world. XYZ is making some strategic changes to the way it operates including changes to staffing structure and introducing more automation. Discuss 4 causes of resistance to change that staff at XYZ may experience and examine how the CEO of XYZ can successfully manage this resistance to change
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Causes of Resistance to Change & Strategies to Manage It – XYZ Case Study
When XYZ, a UK-based toilet paper manufacturer, implementsstrategic changessuch asstaff restructuring and automation, employees mayresist changedue to uncertainty, fear, and disruption to their work environment. Below arefour key causes of resistanceand how theCEO can manage them effectively.
Causes of Resistance to Change
1. Fear of Job Loss
????Cause:Employees may fear thatautomationwill replace their jobs, leading to layoffs. Factory workers and administrative staff may feel particularly vulnerable.
????Example:If machines take over manual processes like paper cutting and packaging, employees may see this as a direct threat to their roles.
2. Lack of Communication and Transparency
????Cause:When managementfails to communicatethe reasons for change, employees may speculate and assume the worst.Unclear messageslead to distrust.
????Example:If XYZ’s CEO announces restructuring without explainingwhyandhowjobs will be affected, employees may feel insecure and disengaged.
3. Loss of Skills and Status
????Cause:Some employees, especiallylong-serving workers, may feel their skills are becoming obsolete due to automation.Managersmay resist change if they fear losing power in a new structure.
????Example:A production line supervisor mayoppose automationbecause it reduces the need for human oversight, making their role seem redundant.
4. Organizational Culture and Habit
????Cause:Employees are accustomed tospecific ways of working, andsudden changes disrupt routine. Resistance occurs when changes challengeexisting work culture.
????Example:XYZ’s employees may havealways used manual processes, and shifting toAI-driven productionfeels unfamiliar and uncomfortable.
How the CEO Can Manage Resistance to Change
1. Effective Communication Strategy
✅What to do?
Clearly explainwhy the changes are necessary(e.g., cost efficiency, competitiveness).
Usetown hall meetings, emails, and team discussionsto provide updates.
Addressemployee concernsdirectly to reduce uncertainty.
????Example:The CEO can sendmonthly updateson automation, ensuring transparency and reducing fear.
2. Employee Involvement and Engagement
✅What to do?
Involve staff indecision-makingto give them a sense of control.
Createcross-functional teamsto gather employee input.
Provide opportunities forfeedback and discussion.
????Example:XYZ canform a worker’s advisory panelto gather employee concerns and address them proactively.
3. Training and Upskilling Programs
✅What to do?
Offertraining programsto help employees adapt to new technologies.
Providereskilling opportunitiesfor employees whose jobs are affected.
Reassure staff that automation willcreate new roles, not just eliminate jobs.
????Example:XYZ can introducedigital skills trainingfor workers transitioning from manual processes to automated systems.
4. Change Champions & Support Systems
✅What to do?
Appointchange champions(influential employees) to advocate for change.
Offeremotional and psychological support(e.g., HR consultations, career guidance).
Recognize and reward employees whoembrace change.
????Example:XYZ can offerbonuses or promotionsto employees who successfully transition into new roles.
Conclusion
Resistance to change is natural, but theCEO of XYZ can minimize resistancethroughclear communication, employee involvement, training, and structured support. By managing resistance effectively, XYZ can ensure asmooth transitionwhile maintaining employee morale and operational efficiency.
XYZ is a manufacturing company based in the UK. It has a large complex supply chain and imports raw materials from Argentina and South Africa. It sells completed products internationally via their website. Evaluate the role of licencing and taxation on XYZ’s operations.
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Evaluation of the Role of Licensing and Taxation on XYZ’s Operations
Introduction
Licensing and taxation play acritical role in international trade, supply chain management, and overall financial performance. For XYZ, aUK-based manufacturing companythat importsraw materials from Argentina and South Africaand sellsinternationally via an e-commerce platform, compliance with licensing and taxation regulations is essential to ensuresmooth operations, cost efficiency, and legal compliance.
This evaluation will assess theimpact of licensing and taxation on XYZ’s global supply chain, import/export activities, and financial performance.
1. The Role of Licensing in XYZ’s Operations
1.1 Import and Export Licensing Regulations
As XYZ importsraw materials from Argentina and South Africa, it must comply with theUK’s import licensing requirementsand trade agreements with these countries.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Import licensesmay be required for certain restricted raw materials (e.g.,metals, chemicals, agricultural products).
Export control lawsmay apply, depending on thedestination of final products.
Delays or finesmay occur if licenses are not properly managed.
????Example:If XYZ importsmetal componentssubject to UK trade restrictions, it mustsecure import licensesbefore shipment clearance.
1.2 Industry-Specific Licensing Requirements
Some industries requirespecial licensesto manufacture and sell products globally.
✅Impact on XYZ:
If XYZ manufactureselectronics or chemical-based products, it may need compliance certifications (e.g.,CE marking in the EU, FDA approval in the US).
Failure to meet licensing requirements canblock international sales.
????Example:A UK manufacturer sellingmedical devicesmust obtainMHRA (Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency) approvalbefore distributing products.
1.3 E-Commerce & Digital Sales Licensing
As XYZ sells its products internationally via itswebsite, it must comply with:✅Consumer Protection Laws(e.g., GDPR for EU customers).✅E-commerce business registrationand online sales regulations.
????Example:XYZ may need aVAT number in the EUif it sells products to European customers via its website.
2. The Role of Taxation in XYZ’s Operations
2.1 Import Duties and Tariffs
XYZ’s supply chain involvesimporting raw materials from Argentina and South Africa, which may attractimport duties and tariffs.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Higherimport duties increase raw material costsand impact profitability.
Tariff-free trade agreements(e.g., UK-South Africa trade deal)may reduce costs.
Post-Brexit UK-EU trade regulationsmay affect supply chain tax structures.
????Example:If theUK imposes high tariffs on South African goods, XYZ may need tofind alternative suppliers or negotiate better deals.
2.2 Corporate Tax & International Tax Compliance
XYZ must comply withUK corporate tax lawsand international taxation regulations.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Payingcorporate tax in the UKbased onglobal sales revenue.
Managinginternational tax obligationswhen selling in multiple countries.
Risk of double taxationif the same income is taxed in multiple jurisdictions.
????Example:If XYZ sells products inGermany and the US, it may need toregister for tax in those countriesand comply withlocal VAT/GST requirements.
2.3 Value Added Tax (VAT) & Sales Tax
Since XYZsells internationally via its website, it must adhere toglobal VAT and sales tax rules.
✅Impact on XYZ:
In theEU, VAT registration is required for online sales above a certain threshold.
In theUS, sales tax regulations varyby state.
Compliance withUK VAT laws (e.g., 20% standard rate)on domestic sales.
????Example:A UK company sellingonline to EU customersmust comply with theEU One-Stop-Shop (OSS) VAT scheme.
2.4 Transfer Pricing & Tax Efficiency
If XYZhas international subsidiaries or supply chain partners, it must managetransfer pricing regulations.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Ensuringfair pricing between UK operations and overseas supplierstoavoid tax penalties.
Optimizingtax-efficient supply chain structurestominimize tax burdens.
????Example:Multinational companies likeApple and Amazonusetax-efficient structuresto reduce liabilities.
3. Strategic Actions for XYZ to Manage Licensing and Taxation Effectively
XYZ can take several steps tooptimize tax compliance and licensing efficiency:
 A screenshot of a computer screen
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer screen
Description automatically generated
Conclusion
Licensing and taxation have amajor impact on XYZ’s international manufacturing and e-commerce operations. To maintain profitability andregulatory compliance, XYZ must:
✅Ensureimport/export licensingaligns with UK and international trade laws.✅Manageimport duties, VAT, and corporate tax obligationseffectively.✅Optimize itssupply chain and tax planningto reduce costs.
By proactively managing these areas, XYZ canenhance its global competitiveness while minimizing risks.
Examine how an organisation can strategically position itself within the marketplace.
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
How an Organization Can Strategically Position Itself in the Marketplace
Strategic positioning is the process by which an organization differentiates itself from competitors and establishes astrong, sustainablepresence in the market. It involves making key decisions regardingbranding, pricing, customer engagement, and competitive advantageto attract and retain customers.
Below are the keystrategies an organization can use to position itself strategically in the marketplace:
1. Competitive Strategy (Porter’s Generic Strategies)
Organizations can useMichael Porter’s Competitive Strategiesto define their market position:
????Cost Leadership– Competing on price by offering the lowest-cost products or services.????Differentiation– Offering unique, high-quality, or innovative products that stand out.????Focus (Niche Strategy)– Targeting a specific market segment with specialized products or services.
????Example:
Aldi(Cost Leadership) keeps prices low by optimizing supply chains.
Apple(Differentiation) uses innovation and brand exclusivity to dominate the premium tech market.
Rolls-Royce(Focus Strategy) targets aniche luxury segmentinstead of mass markets.
2. Strong Branding and Market Perception
Organizations must builda strong brand identityto differentiate themselves. This includes:
✅Consistent Branding– Using logos, colors, and messaging that reinforce identity.✅Emotional Connection– Telling a brand story that resonates with customers.✅Trust and Reputation– Delivering quality products and services to establish credibility.
????Example:
Coca-Colauses global branding to evoke happiness and refreshment, maintaining strong market dominance.
Teslamarkets itself as an innovative,eco-friendlybrand, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
3. Innovation and Product Development
Tomaintain a competitive edge, companies must invest ininnovationand continuously improve their products/services.
✅Technology Adoption– Implementing cutting-edge solutions (e.g., AI, automation).✅Customer-Centric Innovation– Developing products based on customer needs.✅First-Mover Advantage– Being the first to introduce groundbreaking products.
????Example:
Amazon’s AI-driven supply chainensures fast deliveries and high customer satisfaction.
Netflix’s streaming modelrevolutionized entertainment consumption, making it an industry leader.
4. Digital Transformation and Market Reach
Organizations can usedigital tools and platformsto enhance their strategic positioning:
✅E-commerce & Online Presence– Expanding reach beyond physical locations.✅Social Media & Influencer Marketing– Engaging with customers through digital channels.✅Data Analytics– Using customer insights to make strategic decisions.
????Example:
Nike’s e-commerce growthanddirect-to-consumer (DTC) modelstrengthened its competitive position.
Zara’s fast fashion strategy, driven by data analytics, allows quick response to trends.
5. Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Modern consumers prefer brands that demonstratesocial and environmental responsibility. Companies can differentiate themselves by:
✅Sustainable Sourcing– Using eco-friendly materials and ethical suppliers.✅Corporate Ethics– Promoting fair labor practices and social initiatives.✅Carbon Footprint Reduction– Committing to green energy and carbon neutrality.
????Example:
Patagonia’s sustainability-first strategyattracts eco-conscious consumers.
Unilever’s “Sustainable Living Plan”enhances brand loyalty through ethical business practices.
6. Strategic Partnerships and Market Expansion
Organizations canstrengthen their market positionthrough collaborations and global expansion:
✅Mergers & Acquisitions– Gaining market share by acquiring competitors.✅Joint Ventures– Partnering with companies for mutual growth.✅New Market Entry– Expanding into emerging markets.
????Example:
Google acquiring YouTubeenhanced its presence in digital content.
Starbucks’ partnership with Nestléexpanded its global coffee distribution.
Conclusion
Strategic positioning requires aclear understanding of competitive advantage,market needs, andinnovative growth strategies. By leveragingcost leadership, differentiation, branding, innovation, digital transformation, sustainability, and partnerships, organizations cansustain long-term success in a competitive market.
Discuss 5 tasks of strategic management
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Five Key Tasks of Strategic Management
Introduction
Strategic management involvesformulating, implementing, and evaluatinga company's long-term goals to achieve competitive advantage. It ensures that an organization effectively aligns itsresources, capabilities, and market positionto meet its objectives.
The strategic management process can be broken down intofive key tasks:
1. Setting Vision, Mission, and Objectives
Strategic management begins with defining theorganization’s purpose and direction.
✅Vision Statement:Describes thelong-term aspirationsof the business.✅Mission Statement:Outlines thecore purpose and values.✅Objectives:Establishspecific, measurablegoals (e.g., market expansion, profitability targets).
????Example:
Tesla’s visionis to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
XYZ Constructionmight set a strategic objective to become the UK’s leading sustainable housing developer.
2. Environmental Scanning and Analysis
Organizations must assessinternal and external environmentsto identifyopportunities and threats.
✅External Analysis– UsesPESTLE(Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental) andPorter’s Five Forcesto assess market conditions.✅Internal Analysis– UsesVRIO (Value, Rarity, Imitability, Organization)andSWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)to evaluate internal capabilities.
????Example:
Aglobal beverage companymay conduct PESTLE analysis to assessregulatory changes in sugar taxation.
XYZ Constructionmay analyzerising material costsand explorealternative suppliers.
3. Strategy Formulation
After analyzing the environment, the organization develops itsstrategic choices:
✅Corporate-Level Strategy:Determinesgrowth direction(e.g., diversification, mergers, acquisitions).✅Business-Level Strategy:Focuses oncompetitive advantage(e.g.,cost leadership, differentiation, or niche market strategies).✅Functional-Level Strategy:Alignsdepartments(procurement, HR, marketing) with the corporate strategy.
????Example:
XYZ Constructioncould adopt acost leadership strategyby sourcing materials more efficiently.
Applefollows adifferentiation strategyby focusing on innovation and design.
4. Strategy Implementation
Once a strategy is formulated, it must beexecuted effectively.
✅Organizational Structure:Ensures the rightteams and leadershipare in place.✅Change Management:Employees mustaccept and supportthe strategy (overcoming resistance to change).✅Resource Allocation:Financial, technological, and human resources must be assigned effectively.
????Example:
XYZ Constructionmight invest innew project management softwareto improve efficiency.
Amazoncontinuouslyoptimizes its logistics networkto implement its cost leadership strategy.
5. Strategy Evaluation and Control
Organizations mustmonitor performanceto ensure the strategy remains effective.
✅Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):Measure progress (e.g., sales growth, cost reduction).✅Feedback & Adaptation:Adjust strategies based onmarket trends and competitor actions.✅Risk Management:Identify and mitigate risks(e.g., economic downturns, supply chaindisruptions).
????Example:
XYZ Constructionmay review project completion times and adjust its approach for greater efficiency.
McDonald’scontinuously adapts its menu based onregional preferences and customer feedback.
Conclusion
The five key tasks of strategic management—setting objectives, environmental scanning, strategy formulation, strategy implementation, and evaluation—help organizationsachieve long-term success and competitive advantage. Effective strategic management ensures that companiesstay agile in dynamic marketswhile making informed, data-driven decisions.
Evaluate the role of strategic human management in creating competitive advantage for an organisation
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Evaluation of the Role of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) in Creating Competitive Advantage
Introduction
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is theproactive alignment of HR policies withbusiness strategyto achieve long-term success. It focuses on developingtalent, leadership, culture, and employee engagementto enhanceorganizational performance and competitiveness.
By implementingeffective SHRM practices, companies can create asustainable competitive advantagethrough a highly skilled and motivated workforce.
1. The Role of SHRM in Creating Competitive Advantage
1.1 Talent Acquisition and Workforce Planning
✅Why it matters?
Recruiting and retaininghighly skilled employeesis essential for innovation and efficiency.
Workforce planning ensuresthe right people are in the right rolesat the right time.
????Example:Google’s strategic hiring approachfocuses on attractingtop AI and engineering talent, driving innovation in tech.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Builds anexpert workforcethat competitors cannot easily replicate.✔Reducesturnover costsby ensuring long-term retention.
1.2 Employee Development and Training
✅Why it matters?
Continuous learning and skills development enhanceemployee productivity and innovation.
Upskilling employees keeps companies ahead infast-changing industries.
????Example:Amazon’s Career Choice Programinvests in employee training to develop future leaders and improve workforce capabilities.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Enhances organizational agilityby equipping employees withemerging skills.✔Creates a culture ofcontinuous improvement and innovation.
1.3 Performance Management and Employee Engagement
✅Why it matters?
Effective performance management systemsensure employees align with business goals.
Engaged employees aremore productive, motivated, and committedto company success.
????Example:Salesforce’s focus on employee engagementthrough leadership development and internal career growth has resulted in high retention and innovation.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Driveshigh workforce productivityand efficiency.✔Reduces costs related topoor performance and disengagement.
1.4 HR Technology and Data-Driven Decision-Making
✅Why it matters?
Digital HR tools (e.g.,AI-driven recruitment, performance analytics, HR automation) optimize talent management.
Data-driven HR strategies help predictworkforce trends and talent gaps.
????Example:Unilever uses AI-driven HR analyticsto identify high-potential employees and enhance leadership succession planning.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Enablesdata-driven workforce planningfor future growth.✔Increasesefficiency and reduces hiring biases.
1.5 Employee Well-being and Diversity & Inclusion
✅Why it matters?
Work-life balance policies, mental health support, and DEI (Diversity, Equity, Inclusion) programsimprove workplace culture.
Diverse teamsenhance creativity, problem-solving, and innovation.
????Example:Microsoft’s Diversity & Inclusion programshave strengthened its brand and innovation by fostering amore inclusive workforce.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Attractstop global talentwho seek inclusive workplaces.✔Strengthensbrand reputation and employee loyalty.
2. Advantages of Strategic HRM in Competitive Positioning
✅Develops Unique Talent & Expertise– Hard for competitors to replicate.✅Enhances Productivity & Efficiency– Skilled, engaged employees drive better results.✅Supports Business Agility & Innovation– Workforce is adaptable to market changes.✅Builds Strong Employer Brand– Attracts and retains high-quality talent.
????Key Takeaway:SHRM transformsHR from an administrative function to a strategic assetthat creates long-term value.
3. Challenges & Risks of SHRM
❌Implementation Costs– Advanced HR technology and training require investment.❌Resistance to Change– Employees may resist new HR policies.❌Measuring ROI Can Be Complex– Talent development impacts long-term but ishard to quantify.❌Legal & Compliance Risks– Global HR policies mustalign with labor lawsacross different countries.
????Solution:Businesses must integrateHR analytics, leadership buy-in, and cultural change strategiesto overcome these challenges.
4. Conclusion
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) isa key driver of sustainable competitive advantageby:
✅Attracting and retaining top talent.✅Developing a highly skilled, engaged, and innovative workforce.✅Leveraging HR technology and data-driven insights.✅Promoting employee well-being, diversity, and inclusion.
Companies thatprioritize SHRMcreate adynamic, future-ready workforce, ensuring long-term success in competitive markets.
Analyse the GE McKinsey Matrix as a tool to influence directional policy
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Analysis of the GE McKinsey Matrix as a Tool to Influence Directional Policy
Introduction
TheGE McKinsey Matrixis astrategic toolused by businesses toprioritize investments, allocate resources, and influence directional policy. It expands on theBCG Matrixby evaluatingbusiness units or product portfoliosbased on two dimensions:
Industry Attractiveness(external factors such as market growth, competition, and profitability).
Business Unit Strength(internal factors such as brand strength, financial performance, and operational efficiency).
The matrix helps organizationsdecide where to invest, grow, or divest, making it a valuable tool for influencinglong-term strategic direction.
1. Explanation of the GE McKinsey Matrix
TheGE McKinsey Matrixcategorizes business units intonine strategic zones, guiding investment decisions:
|Industry Attractiveness →
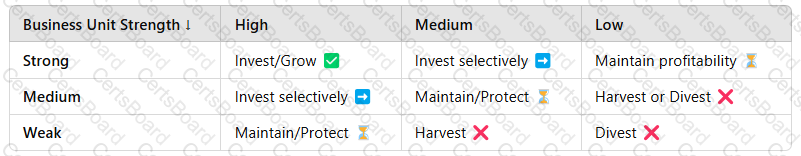 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
Example:
Apple’s iPhone (High Industry, Strong Business Unit)→Invest & Grow????
Microsoft’s Bing Search Engine (Low Industry, Weak Business Unit)→Divest or Harvest❌
2. How the GE McKinsey Matrix Influences Directional Policy
1. Investment Prioritization
✅Identifieswhich business units deserve more investment.✅Helps companies allocate resources tohigh-potential markets.
????Example:Amazon invests heavily inAWS (Cloud Computing)due tohigh industry growth and strong business positioning.
2. Market Entry and Expansion Decisions
✅Assists ingeographical and market expansiondecisions.✅Helps assesswhether to enter emerging industries.
????Example:Tesla enteredrenewable energy (solar panels, batteries)due tohigh industry potential.
3. Strategic Exit or Divestment Decisions
✅Identifieslow-performing divisionsthat should be divested.✅Prevents financial losses byexiting declining markets.
????Example:GE sold its financial services division (GE Capital)to refocus onindustrial manufacturing.
4. Balancing Risk and Portfolio Diversification
✅Encourages abalanced portfolio of high-growth and stable businesses.✅Ensures companiesavoid over-reliance on a single product or market.
????Example:Google (Alphabet)maintains adiverse portfolioofAI, search, and cloud businessesto balance risk.
3. Advantages and Limitations of the GE McKinsey Matrix
✅Advantages✔More detailed than the BCG Matrix– Considers multiple industry and business factors.✔Helps with long-term strategic planning– Guides investment, expansion, and divestment.✔Balances risk and growth– Prevents over-reliance on a single revenue source.
❌Limitations✖Subjective analysis– Industry attractiveness and business strengthare difficult to quantify.✖Complex implementation– Requiresdetailed data collection and industry research.✖No direct action plan– Only providesguidance on resource allocation, not execution strategies.
4. Conclusion
TheGE McKinsey Matrixis a powerful tool forinfluencing directional policyby helping companiesprioritize investments, expand into attractive markets, and exit underperforming businesses. However, it should be used alongsidefinancial analysis and market researchto ensurestrategic success.
Discuss the difference between a merger and an acquisition. What are the main drivers and risks associated with this approach to growth compared to an organic development strategy?
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Mergers vs. Acquisitions: Drivers, Risks, and Comparison to Organic Growth
Introduction
Businesses seeking growth can expand throughmergers and acquisitions (M&A)or byorganic development. Mergers and acquisitions involveexternal growth strategies, where companies combine forces or take over another business, whereas organic growth occursinternally through investment in operations, R&D, and market expansion.
While M&A strategies providerapid expansion and competitive advantages, they also carryintegration risks and financial complexitiescompared to organic growth.
1. Difference Between a Merger and an Acquisition
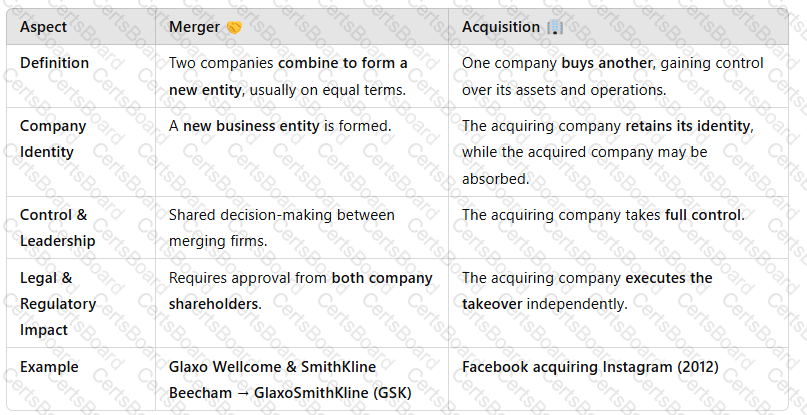 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:Mergers are usuallycollaborative, while acquisitions involveone company dominating another.
2. Main Drivers of Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A)????
1. Market Expansion & Faster Growth
✅Providesimmediate accessto new markets, customers, and geographies.✅Faster than organic growth, allowing firms toscale operations quickly.
????Example:Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foodsgave it an instant presence in the grocerysector.
2. Cost Synergies & Efficiency Gains
✅Reducesduplication of functions(e.g., shared IT, supply chain).✅Achieveseconomies of scale, lowering operating costs.
????Example:Disney’s acquisition of 21st Century Foxreduced production costs by consolidating media assets.
3. Competitive Advantage & Market Power
✅Eliminates competition by absorbingrival firms.✅Strengthensbargaining power over suppliers and distributors.
????Example:Google acquiring YouTuberemoved a major competitor in the video-sharing industry.
4. Access to New Technology & Innovation
✅Fast-tracksadoption of emerging technologies.✅Avoids lengthyin-house R&D developmentcycles.
????Example:Microsoft’s acquisition of LinkedIngave it access to AI-driven professional networking tools.
3. Risks of Mergers & Acquisitions⚠️
1. Cultural & Operational Integration Challenges
❌Employees from different companies mayresist integration, leading to conflicts.❌Different corporate culturesmay result in productivity loss.
????Example:TheDaimler-Chrysler merger faileddue to cultural clashes between German and American management styles.
2. High Financial Costs & Debt Risks
❌Acquiring companiesoften take on large amounts of debt.❌M&A dealsmay overvalue the target company, leading to losses.
????Example:AOL’s acquisition of Time Warner($165 billion) resulted inhuge financial lossesdue to overvaluation.
3. Regulatory and Legal Barriers
❌Government regulators mayblock mergers due to monopoly concerns.❌Legal challenges maydelay or cancel deals.
????Example:TheEU blocked Siemens and Alstom’s rail mergerdue to competition concerns.
4. Disruption to Core Business
❌Management focus on M&A candistract from existing operations.❌Post-merger integration complexitiescan lead to delays and inefficiencies.
????Example:HP’s acquisition of Compaqresulted in years of internal restructuring, impacting performance.
4. Comparison: M&A vs. Organic Growth
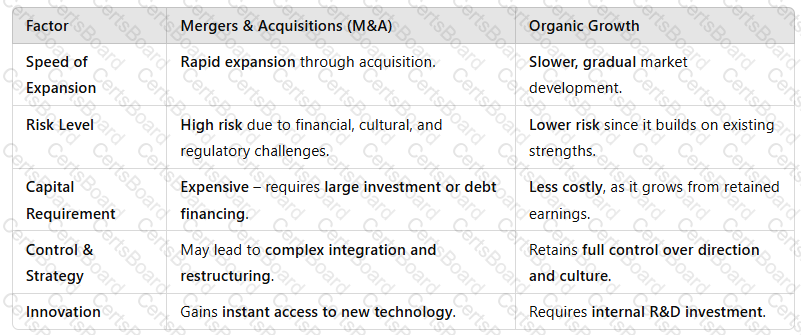 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:M&A providesfast expansionbut comes withhigher risks, whereas organic growth isslower but more sustainable.
5. Conclusion
Mergers and acquisitions offera fast-track to market leadership, providinggrowth, cost synergies, and competitive advantages. However, they also carrysignificant financial, cultural, and regulatory riskscompared to organic growth.
✅Best for:Companies needingrapid expansion, technology access, or competitive positioning.❌Risky when:Poor cultural integration, excessive debt, or regulatory obstacles arise.
Businesses mustcarefully assess strategic fit, financial feasibility, and post-merger integration plansbefore choosing M&A as a growth strategy.
Explain how culture and historic influences can impact upon a business’s strategic decisions and positioning within the marketplace
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
How Culture and Historic Influences Impact Strategic Decisions and Market Positioning
A business’sstrategic decisionsandpositioning within the marketplaceare shaped by bothorganizational cultureandhistorical influences. These factors affect how a companydevelops strategy, interacts with customers, manages employees, and competes globally.
1. The Role of Organizational Culture in Strategic Decisions
Organizational culture is theshared values, beliefs, and behaviorswithin a company. It influencesdecision-making, innovation, and competitive advantage.
????How Culture Affects Strategy
✅Risk Appetite– A culture that embraces innovation (e.g., Google) will invest in R&D, while risk-averse cultures (e.g., traditional banks) focus on stability.✅Decision-Making Speed– Hierarchical cultures (e.g., Japanese firms) rely on consensus, while Western firms (e.g., Apple) may have centralized decision-making.✅Customer Engagement– Acustomer-centric culture(e.g., Amazon) leads to investment in personalization and AI-driven recommendations.
????Example:
Toyota’s Kaizen Culture (Continuous Improvement)has shaped itslean manufacturing strategy, giving it a competitive advantage in cost efficiency.
2. How Historic Influences Shape Business Strategy
Historical events,past business performance, economic trends, and industry evolutionshape how businessesposition themselves in the marketplace.
????How History Affects Strategy
✅Legacy of Innovation or Conservatism– Companies with a history ofinnovation(e.g., IBM, Tesla) continuously push boundaries, while firms with traditional roots (e.g., British banks) focus on risk management.✅Economic Crises and Financial Stability– Businesses that survived financial crises (e.g., 2008 recession) tend to developrisk-averse financial strategies.✅Market Reputation and Consumer Perception– A stronghistorical reputationcan be leveraged for branding (e.g., Rolls-Royce’s luxury image).
????Example:
Legonearly went bankrupt in the early 2000s, leading it toredefine its strategy, focus ondigital gaming partnerships, and revive its brand.
3. The Influence of National and Corporate Culture on Global Positioning
When expanding globally, businesses mustalign their strategies with different cultural expectations.
????How Culture Affects Global Market Entry
✅Consumer Preferences– Fast food chainsadapt menusfor local cultures (e.g., McDonald's in India offers vegetarian options).✅Negotiation & Communication Styles– Business negotiations inChinaemphasize relationships ("Guanxi"), whileWestern firmsprioritize efficiency.✅Leadership and Management Approaches–German firmsemphasize engineering precision, whileSilicon Valley firmsprioritize agility and experimentation.
????Example:
IKEAmodifies store layouts in different countries—small apartments in Japan vs. large home spaces in the U.S.
4. Strategic Positioning Based on Cultural & Historic Factors
A company’s historical and cultural influences define itspositioning strategy:
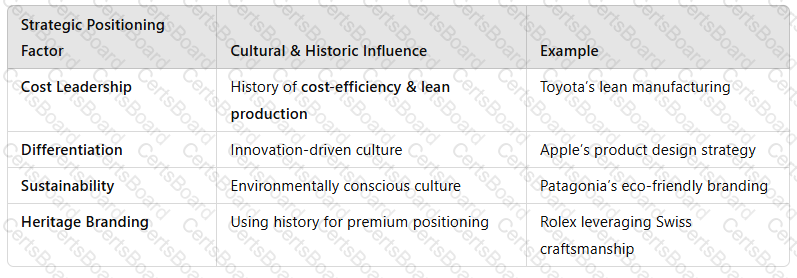 A screenshot of a white box
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a white box
Description automatically generated
Conclusion
A business’sstrategic decisions and market positioningare deeply influenced byorganizational culture, national culture, and historical performance. Companies thatleverage their cultural strengths and adapt to market historycan achievelong-term competitive advantage.

TESTED 01 Apr 2025
Copyright © 2014-2025 CertsBoard. All Rights Reserved



