In a multi-VRF environment, while performing mutual route leaking on the VRRP peers with BGP neighborship established in between and towards the upstream network, the switch installs both routes as ECMP instead of preferring the leaked route.
What happens if a VSF link fails?
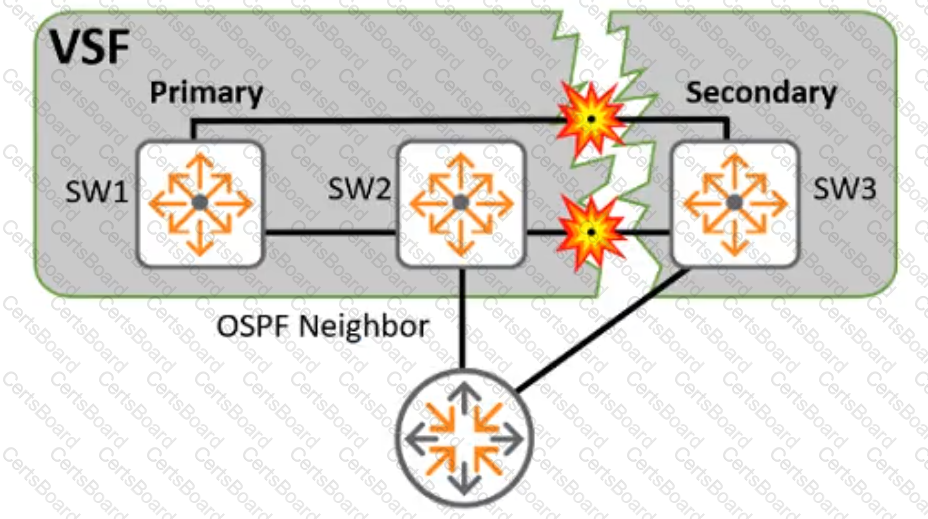
If the stack topology is a ring, it will degenerate to a chain when a VSF link in the stack fails.
If the topology is a chain, a VSF link failure will result in a stack being split into two independent stack fragments.
When a stack splits and the master and standby of the stack become part of two different fragments, the standby takes up the master role for its fragment. Network disruption can result because the two fragments are simultaneously active. Aruba highly recommends enabling VSF split-detection to gracefully handle split brain scenarios.
If a stack splits and the master and standby are in the same fragment with the other members on a different fragment, the members-only fragment will:
What is VSF split-detect?
When a stack splits, the split-detect feature provides a mechanism for the fragments to discover each other.
Once the two stack fragments are discovered, the fragment that has the primary member becomes the active fragment and keeps its front plane (non-VSF) interfaces up and running. The other fragment becomes inactive and all non-VSF interfaces on the inactive fragment are brought down to avoid network disruption.
How do I configure split-detect?
VSF supports split-detection through the management interface.
Connect the management interfaces of the primary and secondary members to the same management VLAN/network or connect them directly to one another. The CLI command to enable split detection is vsf split-detect mgmt.