Following is information related banks:
Auckland Ltd is a public sector bank operating with about 120 branches across India. The bank has been in business since 1971 and has about 40% branches in rural areas and about 75% of all branches are in
Western India. On the basis of the size, Auckland Ltd will be ranked at number 31 amongst 40 banks in India.
Although top management has appointment period of 5 years, generally they retire on ach sieving age of 60 years with an average tenure of only 2 years at the top job.
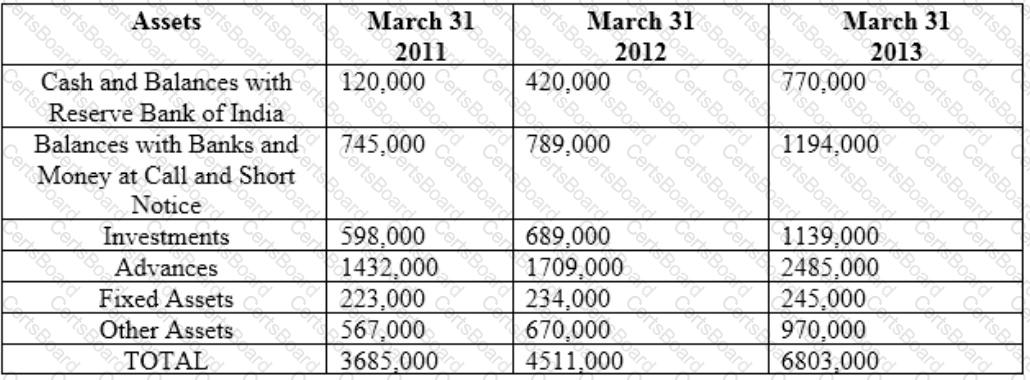
Profit and Loss Account

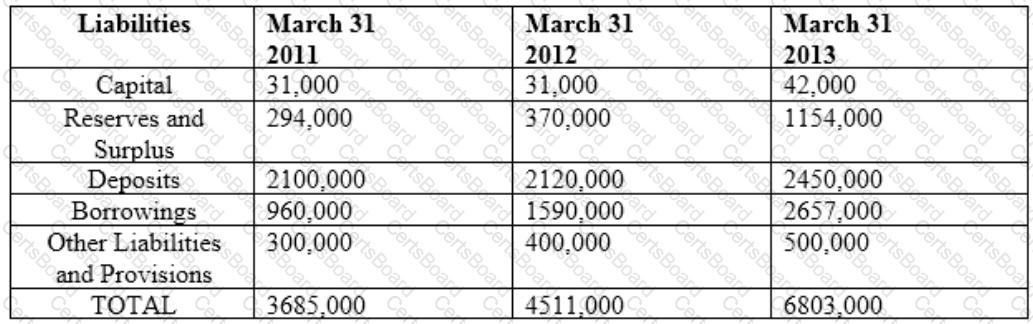
Balance Sheet
The rating wise break-up of assets for FY11 is as follows:

Cost to income ratio is best for which year
Which of the following factor is considered while undertaking management evaluation?
The extension of a guarantee by company A to company B can lower the rating of___________
The following information pertains to bonds:
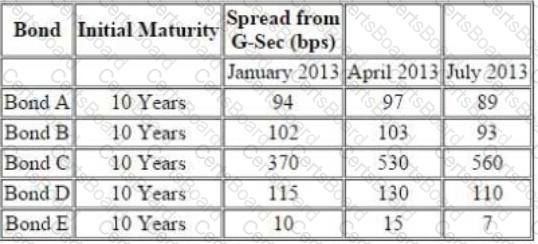
Further following information is available about a particular bond ‘Bond F’
There is a 10.25% risky bond with a maturity of 2.25% year(s) its current price is INR105.31, which corresponds to YTM of 9.22%. The following are the benchmark YTMs.
Following are the relevance of Industry Analysis:
Statement 1: Evaluating Industry risk is the first and foremost step for top down approach of analysis.
Statement 2: Industry Analysis is relevant for analyzing the industry life cycle, which is highly important from
the perspective of an investor or lender.
State which is/are correct?
Scott is a credit analyst with one of the credit rating agencies in India. He was looking in Oil and Gas Industry companies and has presented brief financials for following 4 entities:

Giving equal weightage to all three ratios, determine which of the above entities should be rated highest on a relative scale.
Ms. Mary Brown is a credit rating analyst. She had prepared a detailed report on one of her client, FlyHigh
Airlines Ltd, a company operating chartered aircrafts in India. As she was heading for a meeting with her superior on the matter, coffee spilled over her set of prepared paper(s). As she was getting late for meeting, instead of preparing entire set she could recollect few numbers from her memory and reconstructed following partial financial table:

Compute Interest for FY10 and FY12?
“Following four entities operate in the Indian IT and BPO space. They all are into same segment of providing off-shore analytical services. They all operate on the labour cost-arbitrage in India and the countries of their clients. Following information pertains for the year ended March 31, 2013.
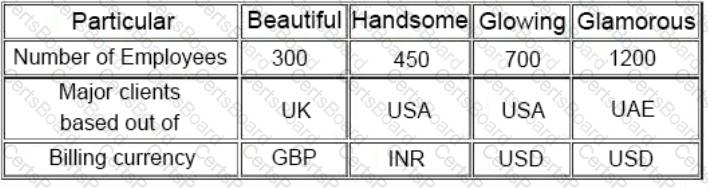

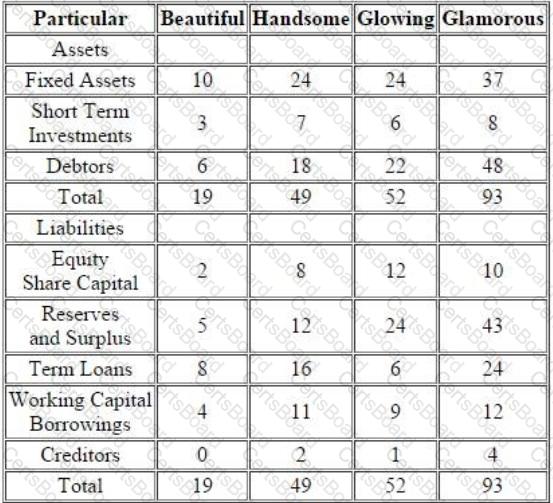
The year FY13, was typically a good year for Indian IT companies. For FY14, the economic analysts have given following predictions about the IT Industry:
A) It is expected that INR will appreciate sharply against other USD.
B) Given high inflation and attrition in IT Industry in India, the wages of IT sector employees will increase more sharply than Inflation and general wage rise in country.
C) US Congress will be passing a bill which restricts the outsourcing to third world countries like India. While analyzing the four entities, you come across following findings related to Glowing:
Glowing is promoted by Mr.M R Bhutta, who has earlier promoted two other business ventures, He started with ABC Entertainment Ltd in 1996 and was promoter and MD of the company. ABC was a listed entity and its share price had sharp movements at the time of stock market scam in late 1990s. In 1999, Mr.Bhutta sold his entire stake and resigned from the post of MD. The stock price declined by about 90% in coming days and has never recovered. Later on in 2003, Mr. Bhutta again promoted a new business, Klear Publications Ltd (KCL) an in the business of magazine publication. The entity had come out with a successful IPO and raised money from public. Thereafter it ran into troubles and reported losses. In 2009, Mr. Bhutta went on to exit this business as well by selling stake to other promoter(s). There have been reports in both instances with allegations that promoters have siphoned off money from listed entities to other group entities, however, nothing has been proved in any court.”
What will be impact of on the predictions A and B of the economic analysts, on companies:
Satish Dhawan, a veteran fixed income trader is conducting interviews for the post of a junior fixed income trader. He interviewed four candidates Adam, Balkrishnan, Catherine and Deepak and following are the answers to his questions.
Question 1: Tell something about Option Adjusted Spread
Adam: OAS is applicable only to bond which do not have any options attached to it. It is for the plain bonds.
Balkishna: In bonds with embedded options, AS reflects not only the credit risk but also reflects prepayment risk over and above the benchmark.
Catherine: Sincespreads are calculated to know the level of credit risk in the bound, OAS is difference between in the Z spread and price of a call option for a callable bond.
Deepark: For callable bond OAS will be lower than Z Spread.
Question 2: This is a spread that must be added to the benchmark zero rate curve in a parallel shift so that the sum of the risky bond’s discounted cash flows equals its current market price. Which Spread I am talkingabout?
Adam: Z Spread
Balkrishna: Nominal Spread
Catherine: Option Adjusted Spread
Deepark: Asset Swap Spread
Question 3: What do you know about Interpolated spread and yield spread?
Adam: Yield spread is the difference between the YTM of a risky bond and the YTM of an on-the-run treasury benchmark bond whose maturity is closest, but not identical to that of risky bond. Interpolated spread is the spread between the YTM of risky bond and the YTM of same maturity treasury benchmark, which is interpolated from the two nearest on-the-run treasury securities.
Balkrishna: Interpolated spread is preferred to yield spread because the latter has the maturity mismatch, which leads to error if the yield curve is not flat and the benchmark security changes over time, leading to inconsistency.
Catherine: Interpolated spread takes account the shape of the benchmark yield curve and therefore better
than yield spread.
Deepak: Both Interpolated Spread and Yield Spread rely on YTM which suffers from drawbacks and inconsistencies such as the assumption of flat yield curve and reinvestment at YTM itself.
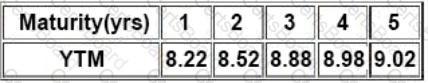
Then Satish gave following information related to the benchmark YTMs:

There is a 10.25% risky bond with a maturity of 4.75 year(s). Its current price is INR105.31, which corresponds
to YTM of 9.22%. Compute Interpolated Spread from the information provided in the vignette:


