A router is trying to establish an IS-IS adjacency with the DIS on a broadcast link. What event causes the adjacency to change from “Initializing” to “UP”?
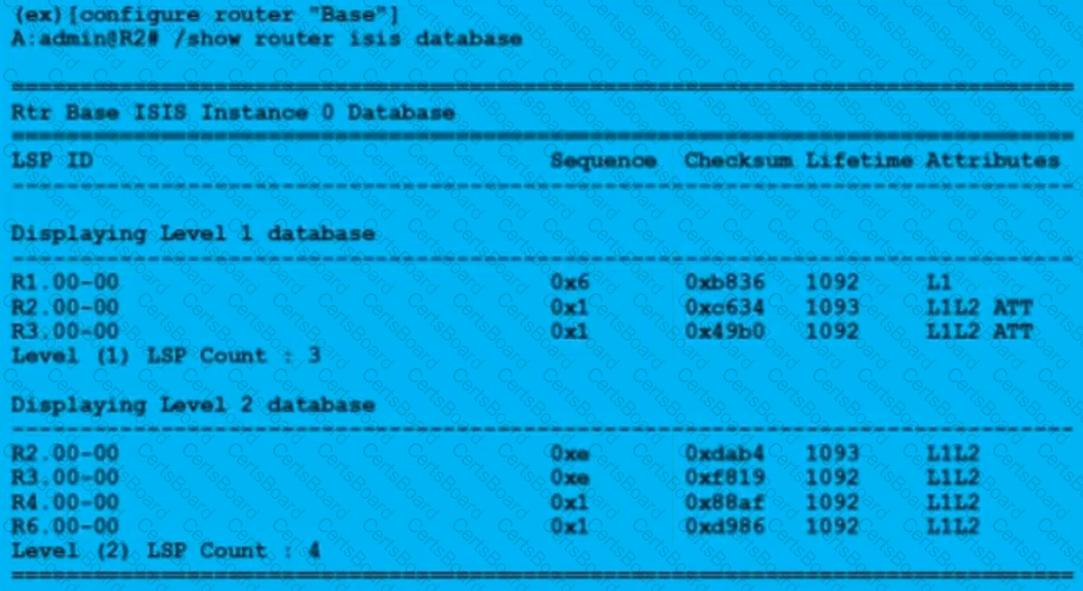
Which of the following statements best describes the IS-IS domain to which the command output corresponds?
A router running a link-state routing protocol detects that one of its neighbors is no longer connected to it. The router generates a new link-state advertisement to inform other routers of the topology change. Which of the following is NOT an action that is triggered by this event?
Which of the following statements about the IP forwarding process on a router is TRUE?
Which of the following statements regarding the databases used by a link-state routing protocol in a single-are routing domain is FALSE?
A routing domain is using a single-area link-state routing protocol. Which of the following is NOT information that a router can share with other routers in the domain using protocol-specific messages?
Consider the exhibit.
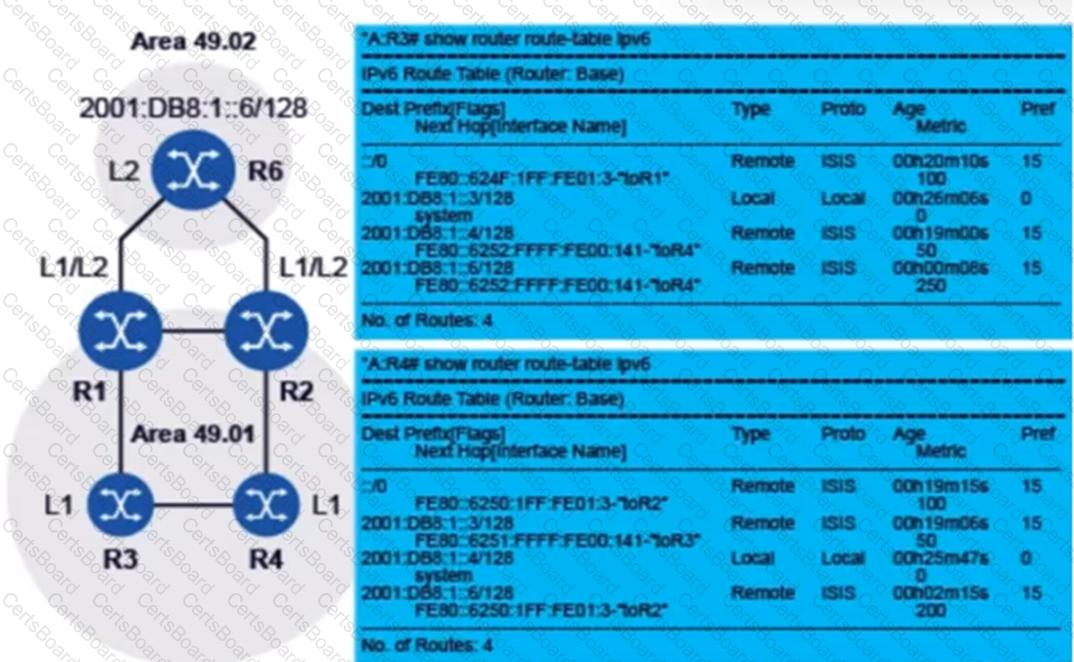
All routers are running IS-IS with IPv6 support enabled. Based on the topology shown, and the route tables of routers R3 and R4, which of the following statements is TRUE?