Which of the following best describes the purpose of the Architecture Requirements Specification?
Please read this scenario prior to answering the question
You are the Lead Enterprise Architect at a major agribusiness company. The company's main harvest is lentils, a highly valued food grown worldwide. The lentil parasite, broomrape, has been an increasing concern for many years and is now becoming resistant to chemical controls. In addition, changes in climate favor the propagation and growth of the parasite. As a result, the parasite cannot realistically be exterminated, and it has become pandemic, with lentil yields falling globally.
In response to the situation, the CEO has decided that the lentil fields will be used for another harvest. The company will also cease to process third-party lentils and will repurpose its processing plants. Thus, the target market will change, and the end-products will be different and more varied.
The company has recently established an Enterprise Architecture practice based on the TOGAF standard as method and guiding framework. The CIO is the sponsor of the activity. A formal request for architecture change has been approved. At this stage there is no fixed scope, shared vision, or objectives.
Refer to the scenario
You have been asked to propose the best approach for architecture development to realize the CEO's change in direction for the company.
Based on the TOGAF standard which of the following is the best answer?
Please read this scenario prior to answering the question
You are working as the Chief Enterprise Architect within a law firm specializing in personal injury cases. Many of the firm's competitors have improved their litigation strategies, and efficiency by streamlining their processes using Artificial Intelligence {Al).
The CIO has approved a Request for Architecture Work to examine the use of Machine Learning in defining a new Al-driven litigation and finance process for the firm. This process would instruct the lawyers and analysts as to what tasks and portfolio they should work on. The key objectives are to increase task profitability, maximize staff utilization, and increase individual profitability.
The CIO has emphasized that the architecture should enable the fast implementation of continuous Machine Learning. The solution will need to be constantly measured for delivered value and be quickly iterated to success.
Some of the partners have expressed concerns about letting the Al make the decisions, others about the risks associated with use of it for the type of service they deliver. The CIO wants to know if these concerns can be addressed, and how risks will be covered by a new architecture enabling Al and Machine Learning.
Refer to the scenario
You have been asked to respond to the CIO recommending an approach that would enable the development of an architecture that addresses the concerns of the CIO and the concerns of the partners.
Based on the TOGAF standard which of the following is the best answer?
Consider the following ADM phases objectives.
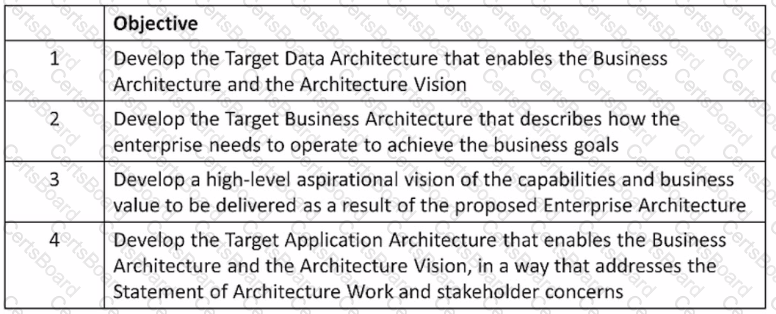
Which phase does each objective match?
Which of the following describes the practice by which the enterprise architecture is managed and controlled at an enterprise-wide level?
Complete the sentence. The architecture domains that are considered by the TOGAF standard as subsets of an overall enterprise architecture are Business, Technology,


